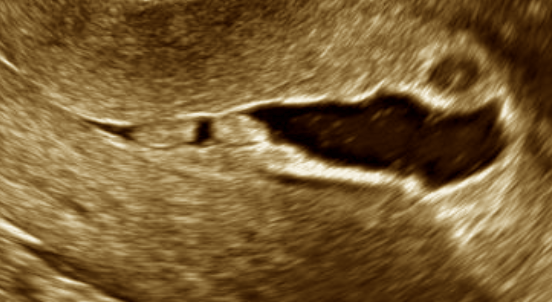
Hysterosonosalpingography (HSSG) is a technique that allows, by the introduction of saline solution through the cervix, to assess the uterine cavity and, in certain circumstances, the fallopian tubes, through a transvaginal ultrasound.
The presence of fluid in the uterine cavity enables the drawing of cavity walls, to determine if they are regular or not, either due to the presence of adenomyosis, polyps or fibroids or if there are endometrial adhesions. Likewise, on certain occasions it can be very useful to exclude the presence of uterine malformations.
As for the fallopian tubes, in expert hands the passage of physiological saline can confirm their patency.
However, the ideal test to verify the tubal patency by transvaginal ultrasound is hysterosonosalpingography with contrast, known as Hysterosalpingo-Contrast-Sonograpy (HyCoSy) or with foam, known as Hysterosalpingo-Foam-Sonographie (HyFoSy).
These techniques allow the uterine cavity and the entire tubal path assessment, by the intrauterine introduction of a contrast solution or foam specially designed for ultrasound evaluation.
When the tubes are intact, the contrast or foam easily reaches the abdominal cavity. When the tubes are blocked, a slowing of the passage and even a blockage can be seen.
HSSG is preferably performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, just after the end of menstrual bleeding and before ovulation. It is essential to exclude any pelvic infection before it is performed and a vaginal or cervical culture can be performed in the event that there is a risk or suspicion of infection. It is recommended a prophylactic antibiotic treatment to avoid ascending infection from possible vaginal germs.
Regarding discomfort, it is milder than pain reported by patients after HSG, what makes it a relatively well tolerated test, although isolated cases of painful uterine contractions, vasovagal reactions, abdominal pain or slight vaginal bleeding have been described.
Contraindications to this technique are pregnancy, active pelvic infection, uterine bleeding, or allergy to components of ultrasound products.
Patients with an allergy to iodinated contrasts and who are not susceptible to HSG, can benefit from these techniques.